



Next: Structure of the Spectral
Up: Spectral Analysis
Previous: Notes on IPC and
Model Spectra for Spectral-Fitting Program
For on-line information type: cl> help using_spectral
The models provided are:
- abs - absorption of x-rays by neutral gas with solar abundances.
| parameter 1 = |
logarithmic value of Galactic NH in units of
cm-2 |
parameter 2 = |
logarithmic value of Intrinsic NH in units of
cm-2 |
parameter 3 = |
redshift of source |
If only one parameter is given, it is assumed to be
the Galactic NH.
If only two parameters are given, they are assumed to be the
Intrinsic NH and the redshift.
- pow - power law
| parameter 1 = |
normalization - logarithmic value of the flux density at
1 keV in units of keV cm-2 s-1 keV-1 |
parameter 2 = |
energy index defined as
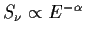 ,
where ,
where 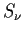 is the flux density
is the flux density |
- bre - thermal bremsstrahlung (exponential plus gaunt factor)
| parameter 1 = |
normalization - logarithmic value of the flux density at
1 keV in units of keV cm-2 s-1 keV-1 |
parameter 2 = |
temperature in the source frame in KeV |
- exp - pure exponential
| parameter 1 = |
normalization - logarithmic value of the flux density at
1 keV in units of keV cm-2 s-1 keV-1 |
| parameter 2 = |
temperature in the source frame in KeV |
- bla - black body
| parameter 1 = |
normalization - logarithmic value of the flux density at
1 keV in units of keV cm-2 s-1 keV-1 |
| parameter 2 = |
temperature in the source frame in keV |
- ray - optically thin thermal spectrum with metallic lines (Raymond code)
| parameter 1 = |
normalization - logarithmic value of the ratio of
the volume emission
measure to
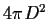 ,
where D is the distance
to the target. Units of the normalization are cm-5. ,
where D is the distance
to the target. Units of the normalization are cm-5. |
parameter 2 = |
temperature in the source frame in keV |
parameter 3 = |
abundance table |
| |
c - cosmic |
| |
m - Meyer |
parameter 4 = |
percentage of heavy elements (100 is the solar value) |
- line - single gaussian line model
| parameter 1 = |
normalization - logarithmic value of the
normalization of the gaussian in units of keV cm-2 s-1. |
| parameter 2 = |
line centroid in keV |
parameter 3 = |
FWHM of the line in keV |
For detailed information on model parameters, please refer to the
science specifications in xspectraldoc$spectral.(tex,dvi).
The spectral model and its parameters are passed to the fitting tasks
as:
absorption(params)*model(params)
More than one absorption and more than one spectral model can be
combined in the following ways:
absorption1(params)*model1(params)+absorption2(params)*model2(params)...
or
absorption(params)*(model1(params)+model2(params)...+modelN(params))
Some basic rules for writing a model description:
NOTE: When different spectral models with different
units for the normalization are combined, the relative normalization of the second
model can be quite large.
For example: ray(1:2,c,100)+pow(11:13,1:2)
specifies a power-law model with a flux of approximately 1% of the
flux in the Raymond model.
See cl> help models_spectral for more information on syntax.
- Note: The program fit starts at the midpoint of the
parameter range specified, then changes the parameters to determine the
direction in which
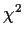 is decreasing and heads in that
direction to find the parameter values that give the minimum
is decreasing and heads in that
direction to find the parameter values that give the minimum 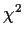 .
If
the initial parameter range is large, only part of the parameter space
may be tested, and the program can settle into a secondary minimum. The
real minimum can be missed. Choose parameter limits
carefully.
.
If
the initial parameter range is large, only part of the parameter space
may be tested, and the program can settle into a secondary minimum. The
real minimum can be missed. Choose parameter limits
carefully.
Examples:
- 1.
- abs(20:21)*pow(1:2)
to describe a power law model spectrum, with energy index varying between
1 and 2, and a galactic absorption varying between
1020 and 1021 cm-2.
- 2.
- abs(20:21,23,1.0)*(pow(1:2)+pow(log(0.5):log(0.6),1.5)
for two power law models, and one absorption applied to both of them.
The galactic absorption can vary
between 1020 and 1021 cm-2, the intrinsic absorption is
fixed at 1023, for an object at z=1. The energy index of the first power
law model can vary between 1 and 2, with the best fit normalization
calculated by the program. The second power law has a fixed index of
1.5, and its normalization is allowed to vary between 50 and 60 % of
the first one.
- 3.
- abs(20:21)*pow(1:2)+abs(21:22)*pow(0.1,2:3)
to describe two power law models, each with galactic absorption in two
different ranges.




Next: Structure of the Spectral
Up: Spectral Analysis
Previous: Notes on IPC and
rsdc@cfa.harvard.edu
1998-06-10